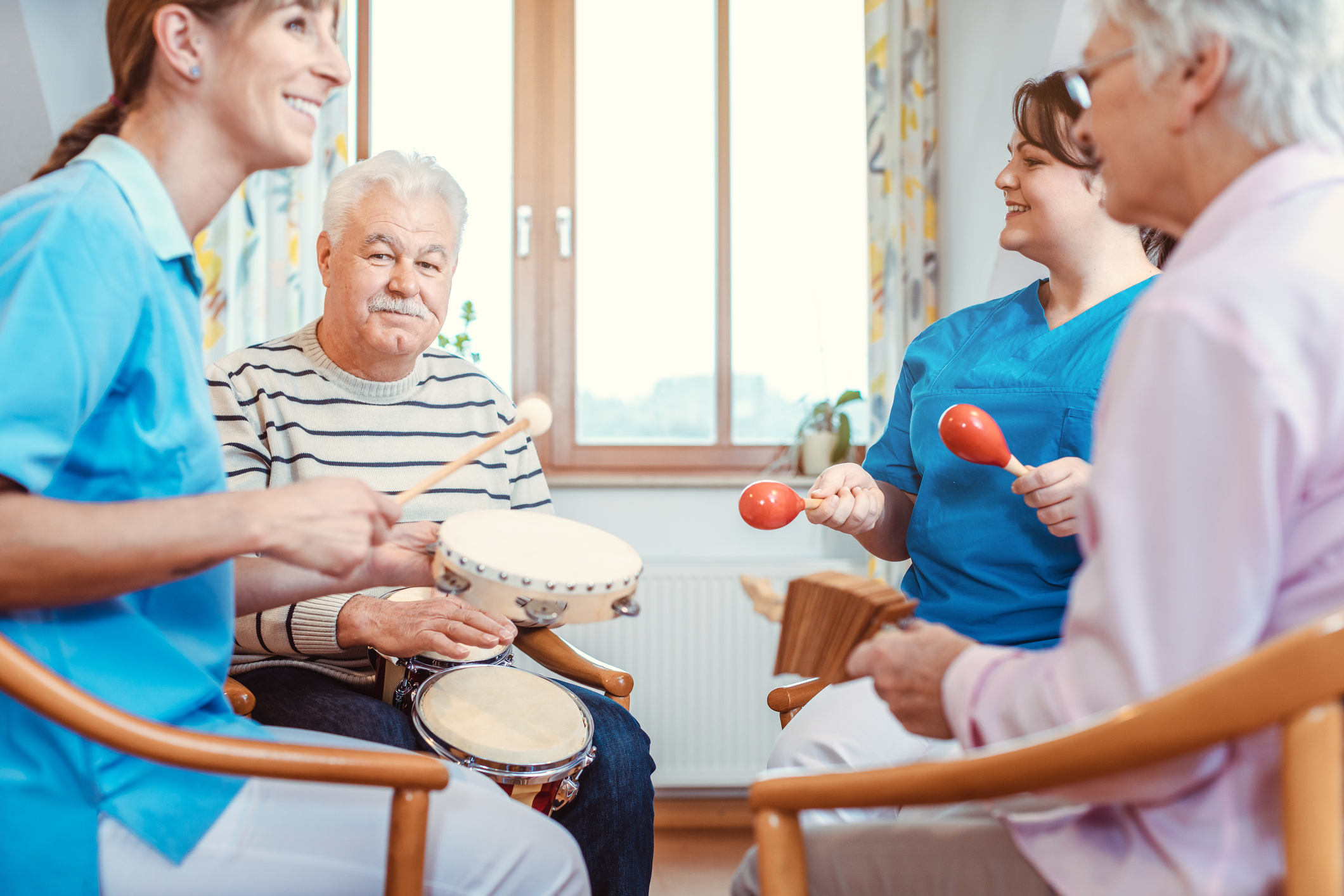
Music Therapy
Therapeutic strategies to provide holistic care to patients include the use of alternative and complementary medicine. Music therapy is an important method to consider with these strategies. The use of music therapy includes playing music for patients or teaching them an instrument to participate in playing music.
Sound healing, which includes music therapy, refers to the more general field of therapeutic sound use, including singing, drumming, rattling, and toning. Sound therapy refers to a practice that is more clinical and structured. Sound healing therapy uses aspects of music to improve physical and emotional health and well-being.
Music therapists assess patients’ emotional well-being, physical health, social functioning, communication abilities, and cognitive skills through musical responses. They then design music sessions for individuals and groups based on the needs assessed using music improvisation, receptive music listening, songwriting, lyric discussion, music and imagery, music performance, and learning through music. Music therapists are an important part of the healthcare team (Harvard Women’s Health, 2016; Ryan, 2017).
Research in music therapy supports its effectiveness in a wide variety of healthcare and educational settings.
Music Therapy Interventions Can be Designed to:
- Promote Wellness
- Manage Stress
- Alleviate Pain
- Express Feelings
- Enhance Memory
- Improve Communication
- Promote Physical Rehabilitation
(American Music Therapy Association [AMTA], 2020)
Music therapy has been shown to be effective with Alzheimer's and dementia, autistic spectral disorders, stroke victims, and in prison populations. In research studies, Alzheimer's patients demonstrate less agitation and confusion when engaged in music exercises. Studies also show autistic children are able to be more expressive and engaging when involved in musical activities. Other studies have shown that patients undergoing invasive procedures who listened to music before their procedure had less anxiety and less need for sedatives. Lost speech from stroke or traumatic brain injury has been improved through music therapy, such as singing. Further studies demonstrated pain management is enhanced, side effects from radiation and chemotherapy are reduced, and physical and emotional functioning during rehabilitation is improved (Harvard Women’s Health, 2016; Ryan, 2017).
Music therapy is not without risks. The AMTA has developed Listening Guidelines for music therapists to consider when initiating a therapy session including, auditory safe, infection control safety, psychological, cognitive, communicative, and sensory limitations (AMTA, 2020).
Healthcare systems across the United States are adopting complementary and alternative therapies into practice. Music therapy, a component of Sound Healing, is increasing in popularity and can lead to gains in emotional well-being, physical health, and communication abilities.
For more information about music therapy and other complementary and alternative medicine techniques, check out the RN.com courses Complementary and Alternative Medicine Part I and Complementary and Alternative Medicine Part II.
References
American Music Therapy Association. (2020). What is music therapy?
Harvard Women’s Health. (2016). How music can help you health.
Ryan, L. (2017). Complementary and Alternative Medicine Part II.